Rhinoplasty
Definition
The term rhinoplasty means "nose molding" or "nose forming." It refers to a procedure in plastic surgery in which the structure of the nose is changed. The change can be made by adding or removing bone or cartilage, grafting tissue from another part of the body, or implanting synthetic material to alter the shape of the nose.
Purpose
Rhinoplasty is most often performed for cosmetic reasons. A nose that is too large, crooked, misshapen, malformed at birth, or deformed by an injury can be given a more pleasing appearance. If breathing is impaired due to the form of the nose or to an injury, it can often be improved with rhinoplasty.
Demographics
Rhinoplasty is the third most common cosmetic procedure among both men and women. Total number of rhinoplasty procedures in the United States in 1999 was 133,058. More than 13,100 of those procedures were performed on men.
Description
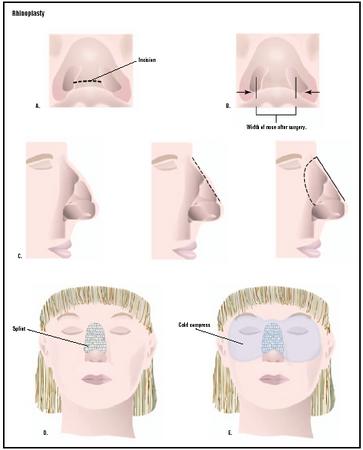
The external nose is composed of a series of interrelated parts that include the skin, the bony pyramid, cartilage, and the tip of the nose, which is composed of cartilage and skin. The strip of skin separating the nostrils is called the columella.
Surgical approaches to nasal reconstruction are varied. Internal rhinoplasty involves making all incisions from inside the nasal cavity. The external, or "open," technique involves a skin incision across the base of the nasal columella. An external incision allows the surgeon to expose the bone and cartilage more fully and is most often used for complicated procedures. During surgery, the surgeon will separate the skin from the bone and cartilage support. The framework of the nose is then reshaped in the desired form. Shape can be altered by removing or adding bone, cartilage, or skin. The remaining skin is then replaced over the new framework. If the procedure requires adding to the structure of the nose, the donated bone, cartilage, or skin can come from another location on the patient's body or from a synthetic source.
When the operation is completed, the surgeon will apply a splint to help the bones maintain their new shape. The nose may also be packed, or stuffed with a dressing, to help stabilize the septum.
When a local anesthetic is used, light sedation is usually given first, after which the operative area is numbed. It will remain insensitive to pain for the length of the surgery. A general anesthetic is used for lengthy or complex procedures, or if the doctor and patient agree that it is the best option.
Diagnosis/Preparation
The quality of the skin plays a major role in the outcome of rhinoplasty. Persons with extremely thick skin
Rhinoplasty should not be performed until the pubertal growth spurt is complete, ages 14–15 for girls and older for boys.
During the initial consultation, the candidate and surgeon will determine what changes can be made in the shape of the nose. Most doctors take photographs during that consult. The surgeon will also explain the techniques and anesthesia options available to the candidate.
The candidate and surgeon should also discuss guidelines for eating, drinking, smoking, taking or avoiding certain medications, and washing the face for the weeks immediately following surgery.
Aftercare
Patients usually feel fine immediately after surgery. As a precaution, most surgery centers do not allow patients to drive themselves home after an operation.
The first day after surgery, there will be some swelling of the face. Persons should stay in bed with their heads elevated for at least a day. The nose may hurt and a headache is common. The surgeon will prescribe medication to relieve these conditions. Swelling and bruising around the eyes will increase for a few days, but will begin to diminish after about the third day. Slight bleeding and stuffiness are normal, and vary according to the extent of the surgery performed. Most people are walking in two days, and back to work or school in a week. No strenuous activities are allowed for two to three weeks.
Patients are given a list of postoperative instructions, which include requirements for hygiene, exercise , eating, and follow-up visits to the doctor. Patients should not blow their noses for the first week to avoid disruption of healing. It is extremely important to keep the surgical dressing dry. Dressings, splints, and stitches are removed in one to two weeks. Patients should avoid excessive sun or sunburn.
Risks
Any type of surgery carries a degree of risk. There is always the possibility of unexpected events such as an infection or a reaction to the anesthesia.
When the nose is reshaped or repaired from inside, the scars are not visible. If the surgeon needs to make the incision on the outside of the nose, there will be some slight scarring. In addition, tiny blood vessels may burst, leaving small red spots on the skin. These spots are barely visible, but may be permanent.
Normal results
The best candidates for rhinoplasty are those persons with relatively minor deformities. Nasal anatomy and proportions are quite varied and the final look of any rhinoplasty operation depends on a person's anatomy, as well as the surgeon's skill.
A cosmetic change of the nose will change a person's appearance, but it will not change self-image. A person who expects a different lifestyle after rhinoplasty is likely to be disappointed.
The cost of rhinoplasty depends on the difficulty of the work required and on the specialist chosen. If the problem was caused by an injury, insurance will usually cover the cost. A rhinoplasty done only to change a person's appearance is not usually covered by insurance.
Morbidity and mortality rates
Death from a rhinoplasty procedure is exceedingly rare. When it occurs, the cause is often due to an adverse reaction to anesthesia or postoperative medications or to an infection. About 10% of persons receiving rhinoplasty require a second procedure.
Alternatives
The alternative to cosmetic rhinoplasty is to accept oneself, literally, at face value. Persons contemplating rhinoplasty may want to question some of the conventional standards of beauty and work on their body image issues to improve their self-confidence.
See also Blepharoplasty ; Forehead lift .
Resources
books
Engler, Alan M. BodySculpture: Plastic Surgery of the Body for Men and Women, 2nd Edition. Poughkeepsie, NY: Hudson Pub, 2000.
Irwin, Brandith, and Mark McPherson. Your Best Face: Looking Your Best without Plastic Surgery. Carlsbad, CA: Hay House, Inc, 2002.
Man, Daniel, and L. C. Faye. New Art of Man: Faces of Plastic Surgery: Your Guide to the Latest Cosmetic Surgery Procedures, 3rd Edition. New York: BeautyArt Press, 2003.
Papel, I. D., and S. S. Park. Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, 2nd Edition. New York: Thieme Medical Publishers, 2000.
periodicals
Ahn, M. S., C. S. Maas, and N. Monhian. "A Novel, Conformable, Rapidly Setting Nasal Splint Material: Results of a Prospective Study." Archives of Facial Plastic Surgery 5, no.2 (2003): 189–192.
Bagal, A. A., and P. A. Adamson. "Revision Rhinoplasty." Facial Plastic Surgery 18, no.4 (2002): 233–244.
Lascaratos, J. G., J. V. Segas, C. C. Trompoukis, and D. A. Assimakopoulos. "From the Roots of Rhinology: The Reconstruction of Nasal Injuries by Hippocrates." Annals of Otolology Rhinology and Laryngology 112, no.2 (2003): 159–162.
Rohrich, R. J., and A. R. Muzaffar. "Rhinoplasty in the African-American Patient." Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 111, no.3 (2003): 1322–1339.
Russell, P., and C. Nduka. "Digital Photography for Rhinoplasty." Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 111, no.3 (2003): 1266–1267.
organizations
American Board of Plastic Surgery. Seven Penn Center, Suite 400, 1635 Market Street, Philadelphia, PA 19103-2204. (215) 587-9322. http://www.abplsurg.org/ .
American College of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. http://www.breast-implant.org .
American College of Surgeons. 633 North Saint Claire Street, Chicago, IL 60611. (312) 202-5000. http://www.facs.org/ .
American Society for Aesthetic Plastic Surgery. 11081 Winners Circle, Los Alamitos, CA 90720. (800) 364-2147 or (562) 799-2356. http://www.surgery.org/ .
American Society for Dermatologic Surgery. 930 N. Meacham Road, P.O. Box 4014, Schaumburg, IL 60168-4014. (847) 330-9830. http://www.asds-net.org .
American Society of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgeons. 44 E. Algonquin Rd., Arlington Heights, IL 60005. (847) 228-9900. http://www.plasticsurgery.org .
American Society of Plastic Surgeons. 444 E. Algonquin Rd., Arlington Heights, IL 60005. (888) 475-2784. http://www.plasticsurgery.org/ .
other
American Academy of Facial and Reconstructive Plastic Surgery. [cited April 9, 2003]. http://www.facial-plasticsurgery.org/patient/procedures/rhinoplasty.html .
National Library of Medicine. [cited April 9, 2003]. http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/plasticcosmeticsurgery.html .
Restoration of Appearance Trust. [cited April 9, 2003]. http://www.raft.ac.uk/plastics/rhinoplasty.html .
Revision Rhinoplasty. [cited April 9, 2003]. http://www.revisionrhinoplasty.net/ .
L. Fleming Fallon, Jr. MD, DrPH
WHO PERFORMS THE PROCEDURE AND WHERE IS IT PERFORMED?
Simple rhinoplasty is usually performed in an outpatient surgery center or in the surgeon's office. Most procedures take only an hour or two, and patients go home right away. Complex procedures may be performed in a hospital and require a short stay.
Rhinoplasty is usually performed by a surgeon with advanced training in plastic and reconstructive surgery.
QUESTIONS TO ASK THE DOCTOR
- What will be the resulting appearance? (Often, computer programs are available to assist in visualizing the final result.)
- Is the surgeon board certified in plastic and reconstructive surgery?
- How many rhinoplasty procedures has the surgeon performed?
- What is the surgeon's complication rate?
- Will this surgery really make a huge difference to my life or am I trying to live up to an impossible media stereotype of beauty?
can u please give me the name of doctores in tunisia for doing this kind of surgry
and send the prices for this kind of surgry
thanx